Pronatalistic alarmism about an oncoming economic crisis driven by a decline in birth rates is largely unfounded. In reality, the average number of children per woman in the US has stayed relatively consistent in recent decades, and technological advancements and increased workforce participation mean that the proportion of workers can remain stable at lower fertility rates.
by Leslie Root, Karen Benjamin Guzzo, and Shelley Clark
Pronatalism – the belief that low birth rates are a problem that must be reversed – is having a moment in the U.S.
As birth rates decline in the U.S. and throughout the world, voices from Silicon Valley to the White House are raising concerns about what they say could be the calamitous effects of steep population decline on the economy. The Trump administration has said it is seeking ideas on how to encourage Americans to have more children as the U.S. experiences its lowest total fertility rate in history, down about 25% since 2007.
As demographers who study fertility, family behaviors and childbearing intentions, we can say with certainty that population decline is not imminent, inevitable or necessarily catastrophic.
The population collapse narrative hinges on three key misunderstandings. First, it misrepresents what standard fertility measures tell us about childbearing and makes unrealistic assumptions that fertility rates will follow predictable patterns far into the future. Second, it overstates the impact of low birth rates on future population growth and size. Third, it ignores the role of economic policies and labor market shifts in assessing the impacts of low birth rates.
Fertility fluctuations
Demographers generally gauge births in a population with a measure called the total fertility rate. The total fertility rate for a given year is an estimate of the average number of children that women would have in their lifetime if they experienced current birth rates throughout their childbearing years.
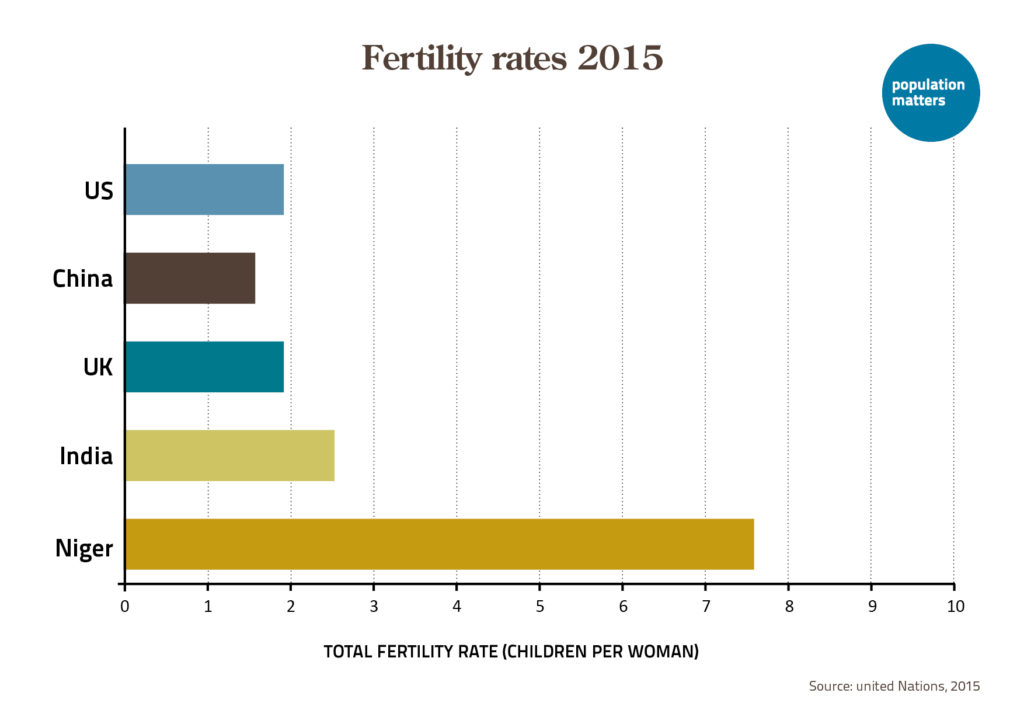
Fertility rates are not fixed – in fact, they have changed considerably over the past century. In the U.S., the total fertility rate rose from about 2 births per woman in the 1930s to a high of 3.7 births per woman around 1960. The rate then dipped below 2 births per woman in the late 1970s and 1980s before returning to 2 births in the 1990s and early 2000s.
Since the Great Recession that lasted from late 2007 until mid-2009, the U.S. total fertility rate has declined almost every year, with the exception of very small post-COVID-19 pandemic increases in 2021 and 2022. In 2024, it hit a record low, falling to 1.6. This drop is primarily driven by declines in births to people in their teens and early 20s – births that are often unintended.
But while the total fertility rate offers a snapshot of the fertility landscape, it is not a perfect indicator of how many children a woman will eventually have if fertility patterns are in flux – for example, if people are delaying having children.
Picture a 20-year-old woman today, in 2025. The total fertility rate assumes she will have the same birth rate as today’s 40-year-olds when she reaches 40. That’s not likely to be the case, because birth rates 20 years from now for 40-year-olds will almost certainly be higher than they are today, as more births occur at older ages and more people are able to overcome infertility through medically assisted reproduction.
A more nuanced picture of childbearing
These problems with the total fertility rate are why demographers also measure how many total births women have had by the end of their reproductive years. In contrast to the total fertility rate, the average number of children ever born to women ages 40 to 44 has remained fairly stable over time, hovering around two.
Americans continue to express favorable views toward childbearing. Ideal family size remains at two or more children, and 9 in 10 adults either have, or would like to have, children. However, many Americans are unable to reach their childbearing goals. This seems to be related to the high cost of raising children and growing uncertainty about the future.
In other words, it doesn’t seem to be the case that birth rates are low because people are uninterested in having children; rather, it’s because they don’t feel it’s feasible for them to become parents or to have as many children as they would like.
The challenge of predicting future population size
Standard demographic projections do not support the idea that population size is set to shrink dramatically.
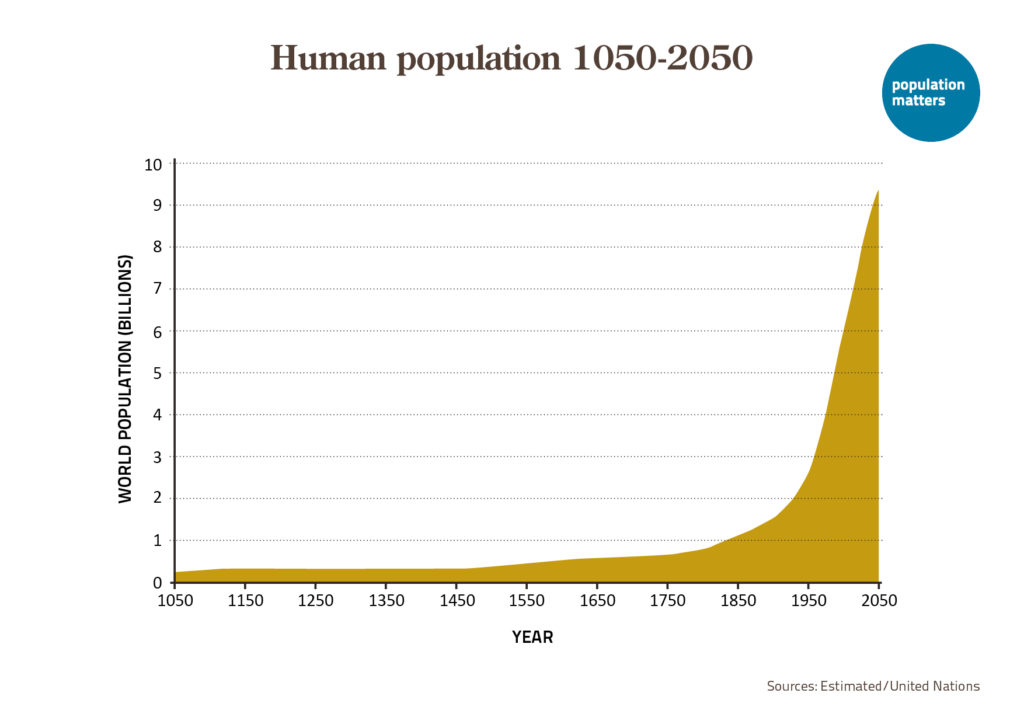
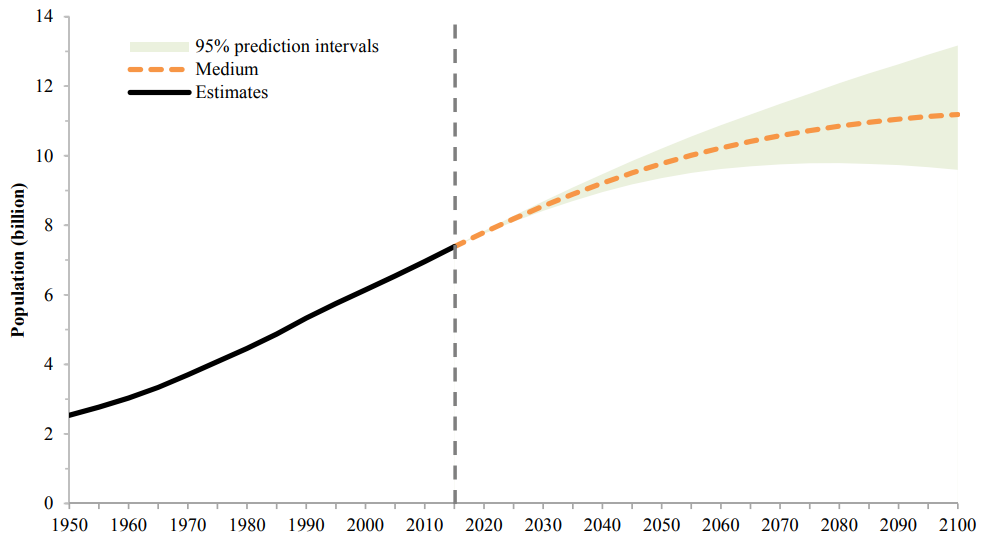
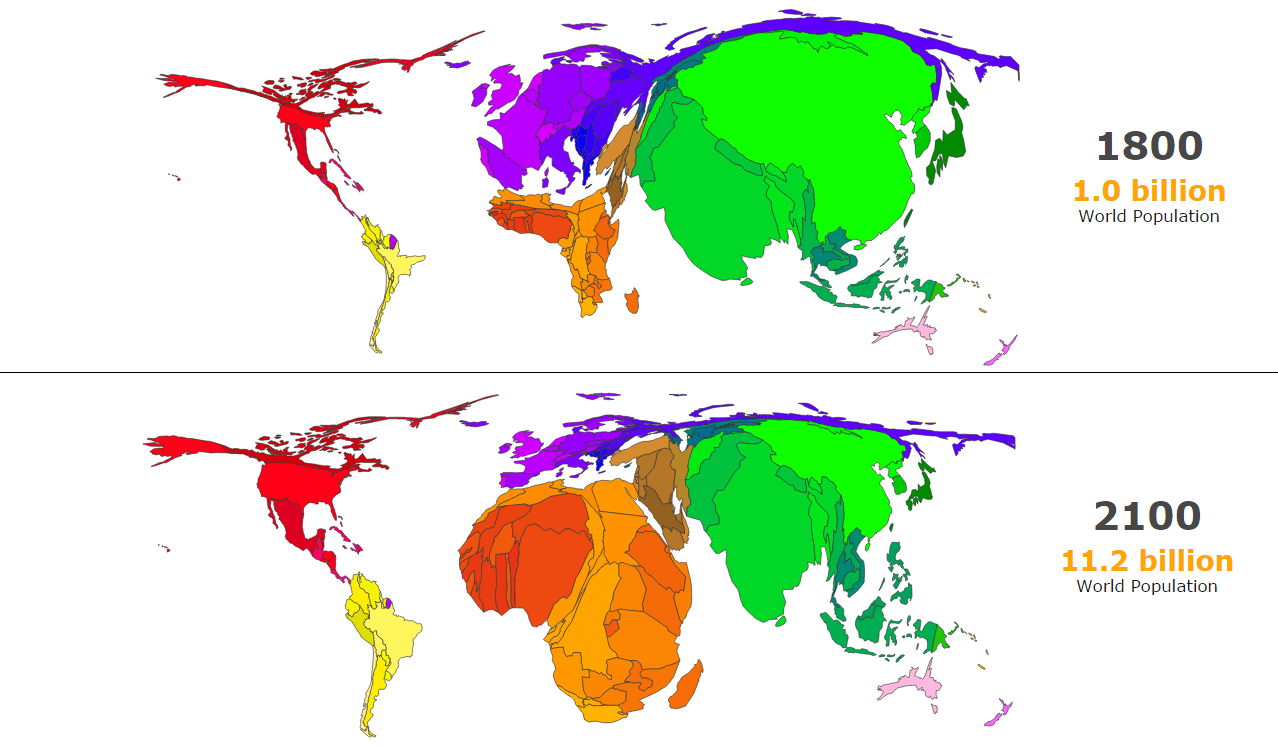
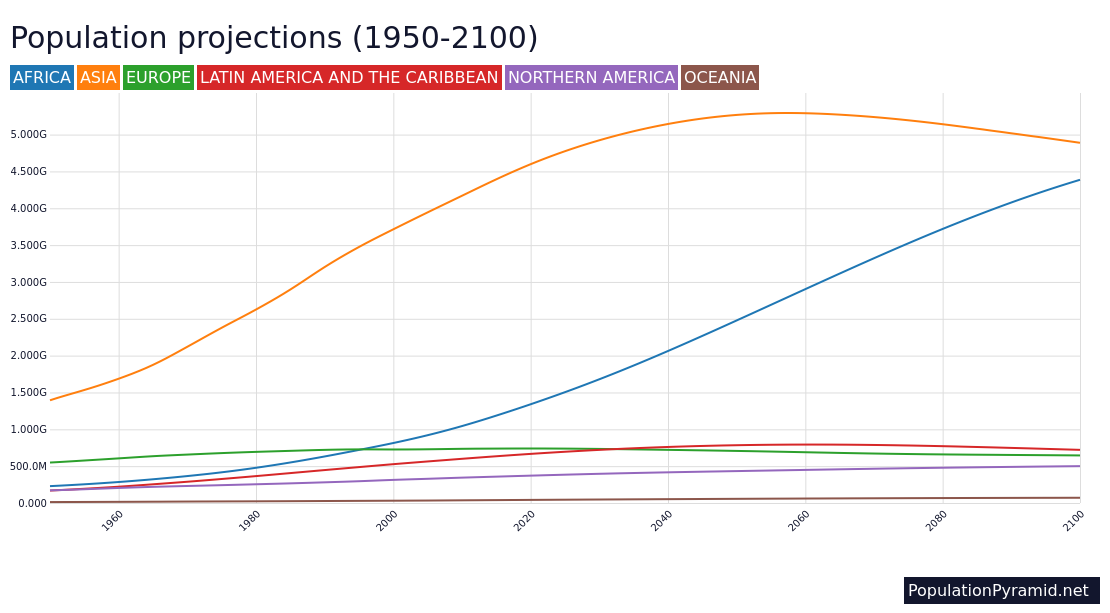
One billion people lived on Earth 250 years ago. Today there are over 8 billion, and by 2100 the United Nations predicts there will be over 10 billion. That’s 2 billion more, not fewer, people in the foreseeable future. Admittedly, that projection is plus or minus 4 billion. But this range highlights another key point: Population projections get more uncertain the further into the future they extend.
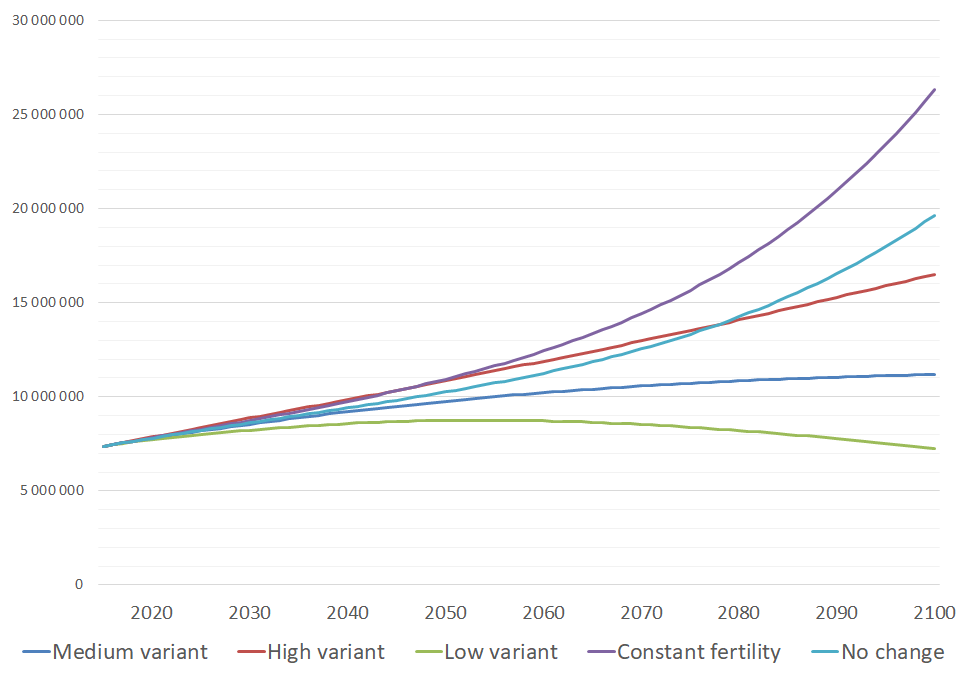
Predicting the population level five years from now is far more reliable than 50 years from now – and beyond 100 years, forget about it. Most population scientists avoid making such long-term projections, for the simple reason that they are usually wrong. That’s because fertility and mortality rates change over time in unpredictable ways.
The U.S. population size is also not declining. Currently, despite fertility below the replacement level of 2.1 children per woman, there are still more births than deaths. The U.S. population is expected to grow by 22.6 million by 2050 and by 27.5 million by 2100, with immigration playing an important role.

Will low fertility cause an economic crisis?
A common rationale for concern about low fertility is that it leads to a host of economic and labor market problems. Specifically, pronatalists argue that there will be too few workers to sustain the economy and too many older people for those workers to support. However, that is not necessarily true – and even if it were, increasing birth rates wouldn’t fix the problem.
As fertility rates fall, the age structure of the population shifts. But a higher proportion of older adults does not necessarily mean the proportion of workers to nonworkers falls.
For one thing, the proportion of children under age 18 in the population also declines, so the number of working-age adults – usually defined as ages 18 to 64 – often changes relatively little. And as older adults stay healthier and more active, a growing number of them are contributing to the economy. Labor force participation among Americans ages 65 to 74 increased from 21.4% in 2003 to 26.9% in 2023 — and is expected to increase to 30.4% by 2033. Modest changes in the average age of retirement or in how Social Security is funded would further reduce strains on support programs for older adults.
What’s more, pronatalists’ core argument that a higher birth rate would increase the size of the labor force overlooks some short-term consequences. More babies means more dependents, at least until those children become old enough to enter the labor force. Children not only require expensive services such as education, but also reduce labor force participation, particularly for women. As fertility rates have fallen, women’s labor force participation rates have risen dramatically – from 34% in 1950 to 58% in 2024. Pronatalist policies that discourage women’s employment are at odds with concerns about a diminishing number of workers.
Research shows that economic policies and labor market conditions, not demographic age structures, play the most important role in determining economic growth in advanced economies. And with rapidly changing technologies like automation and artificial intelligence, it is unclear what demand there will be for workers in the future. Moreover, immigration is a powerful – and immediate – tool for addressing labor market needs and concerns over the proportion of workers.
Overall, there’s no evidence for Elon Musk’s assertion that “humanity is dying.” While the changes in population structure that accompany low birth rates are real, in our view the impact of these changes has been dramatically overstated. Strong investments in education and sensible economic policies can help countries successfully adapt to a new demographic reality.
This article was first published by The Conversation on 25 July 2025.













Leave a Reply